Navigating Vitamin C Forms: A Formulator's Guide to Ascorbic Acid, Sodium Ascorbate, and Calcium Ascorbate
For product developers, selecting the right vitamin C source is key. This guide compares ascorbic acid, sodium ascorbate, and calcium ascorbate across critical parameters like pH and bioavailability, providing actionable insights for your formulation strategy.

The Formulator's Dilemma: Beyond Basic Vitamin C Supplementation
The global demand for vitamin C ingredients—with L-ascorbic acid valued at approximately $1.389 billion in 2024—highlights its pervasive role across nutraceutical, functional food, and cosmetic industries (QYResearch, 2024). For B2B brands seeking market distinction, however, simply listing "vitamin C" on a label is insufficient. True competitive advantage hinges on the strategic selection of the specific chemical form. This decision directly governs critical commercial outcomes: production stability, sensory profile, consumer compliance (driven by tolerability), and the substantiation of clinical efficacy claims. Choosing between ascorbic acid, sodium ascorbate, and calcium ascorbate is thus a fundamental formulation and business strategy, impacting cost-in-use, label claims, and target market appeal.
Deconstructing the Vitamin C Family: A Technical Profile
At its core, all bioavailable vitamin C is L-ascorbic acid or its derivatives. The different powder forms available to manufacturers are either the pure acid or its mineral salts, each modifying the compound's physical and chemical properties with direct commercial implications.
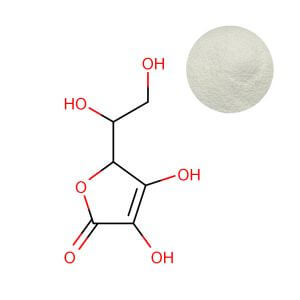
Ascorbic Acid: The Potent Standard
Pure ascorbic acid powder is the benchmark. It delivers the highest concentration of active vitamin C by weight (nearly 100%), offering the most cost-effective potency for high-dose applications like classic supplement tablets and capsules. This high potency translates to lower inclusion rates for a given dose, a key factor in cost-sensitive formulations. Its highly acidic nature (pH around 2.5 in solution), however, presents significant formulation hurdles. Beyond causing gastrointestinal discomfort in a notable subset of consumers—reported in up to 20% of individuals taking high doses (Padayatty et al., 2016, doi:10.3945/an.115.011080)—this acidity can destabilize pH-sensitive ingredients in complexes, accelerate oxidation in liquid formats (requiring costly stabilization systems), and impair flavor, increasing reliance on masking agents.
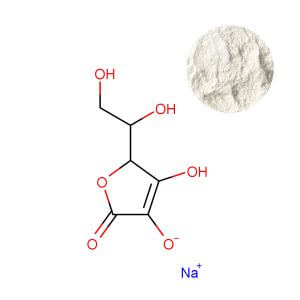
Sodium Ascorbate: The Neutralized Workhorse
Sodium ascorbate powder is formed by buffering ascorbic acid with sodium, yielding a pH-neutral or slightly alkaline compound (pH ~7.0-7.5). This solves the primary issues of gastric irritation and formulation acidity. It is the indispensable form for effervescent products, where its predictable reaction with citric acid creates the desired fizz without excessive sourness. Formulators also favor it in liquid multivitamins and ready-to-mix powder blends where a neutral pH is crucial for the stability of other nutrients and overall palatability. The trade-off is a slightly lower vitamin C content by weight (approximately 89%) and the addition of approximately 111mg of sodium per 1000mg of ascorbate. This sodium content, while often beneficial in electrolyte or sports nutrition products, requires careful consideration for products targeting sodium-restricted populations and must be factored into final label declarations.
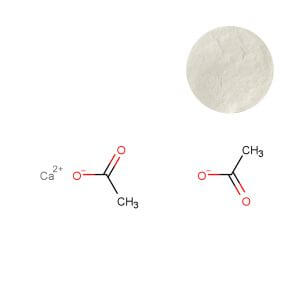
Calcium Ascorbate: The Mineral-Fortified Alternative
Calcium ascorbate powder buffers ascorbic acid with calcium, resulting in a non-acidic, stomach-gentle compound. Its defining commercial feature is dual-nutrient delivery: it provides approximately 82-90% vitamin C and about 90-100mg of elemental calcium per 1000mg of ascorbate. This creates an intelligent value proposition for bone health complexes, multivitamins for older adults, or any formulation where supplementing both nutrients synergistically justifies a premium positioning. Specialized forms, such as calcium ascorbate bound with L-threonate (e.g., Ester-C®), are supported by clinical research indicating superior gastrointestinal tolerability and improved retention within white blood cells compared to plain ascorbic acid (Marini et al., 2025, doi:10.3390/nu17020279), enabling strong "gentle yet effective" marketing claims.
The Comparative Matrix: Key Selection Criteria for Formulators
The optimal choice depends on aligning the raw material's properties with the finished product's technical and commercial goals. The following table synthesizes the critical decision factors:
| Parameter | Ascorbic Acid | Sodium Ascorbate | Calcium Ascorbate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Active Vitamin C Content | Highest (~99%) | High (~89%) | Moderate (~82-90%) |
| pH (in solution) | Highly Acidic (~2.5) | Neutral to Alkaline (~7.0-7.5) | Neutral to Alkaline (~6.5-7.5) |
| Key Mineral Delivered | None | Sodium (~11%) | Calcium (~10%) |
| Typical Cost-in-Use | Lowest (highest potency) | Moderate | Moderate to Higher (premium forms) |
| GI Tolerability | Potentially irritating for some | Generally well-tolerated | Excellent; clinically shown to cause fewer adverse events |
| Primary Application Sweet Spots | High-potency tablets/capsules, acidic food systems, cost-driven blends | Effervescent tablets, liquid formulas, pH-sensitive blends, electrolyte products | Bone/joint health formulas, gentle multivitamins, mineral-fortified products, premium immune complexes |
Formulation in Focus: Translating Theory into Product Performance
Understanding these profiles allows developers to solve real-world formulation challenges proactively, balancing science with production pragmatism.
Maximizing Bioavailability and Cellular Uptake
The commercial promise of a vitamin C product hinges on its biological efficacy. While plasma levels are important, functional benefits like immune support are linked to cellular uptake, particularly in leukocytes. Research on specialized mineral ascorbates, like the calcium ascorbate-threonate complex, demonstrates enhanced retention in white blood cells (Marini et al., 2025, doi:10.3390/nu17020279). For a formulator, this translates into a tangible product differentiator. Investing in a form with clinically supported cellular bioavailability allows for stronger, more defensible claims—such as "advanced cellular support"—compared to products using standard ascorbic acid, moving beyond mere potency to efficacy storytelling.
Mastering Stability in Complex Systems
Stability is a direct determinant of shelf life, cost, and brand reputation. Vitamin C degradation via oxidation is accelerated by heat, light, metal ions, and—critically—low pH. In a neutral-pH liquid multivitamin, using acidic ascorbic acid can destabilize other pH-sensitive ingredients (e.g., some B vitamins) and catalyze its own breakdown, leading to potency loss and potential color/flavor changes. Switching to sodium or calcium ascorbate stabilizes the entire system's pH, reducing oxidative stress and extending viable shelf life, which reduces waste and protects brand integrity. In dry blends for functional foods or powders, the lower hygroscopicity (moisture attraction) of mineral ascorbates compared to pure ascorbic acid can significantly improve powder flowability, prevent caking, and ensure consistent dosing in automated production lines.
Engineering Superior Sensory Experience
Consumer adherence is won or lost on taste and mouthfeel. The intense sourness of ascorbic acid often requires high levels of sweeteners and complex flavor-masking systems in gummies, drink powders, or chewables, increasing cost and conflicting with clean-label trends. The neutral taste profile of buffered ascorbates simplifies flavor systems, reduces added sugar needs, and supports cleaner labels. In effervescent applications, sodium ascorbate's predictable reaction kinetics are essential for achieving a consistent, pleasant fizz with no residual acidic bite, directly impacting consumer satisfaction and repeat purchases.
Strategic Application Pathways: Matching Form to Function
The most innovative applications leverage the unique benefits of each form to meet specific market needs and create compelling brand propositions.
- Next-Generation Immune & Wellness Formulas: Beyond megadose capsules, developers are creating targeted daily support complexes. A formula using a well-researched calcium ascorbate (like a calcium ascorbate-threonate complex), combined with zinc and immune-modulating botanicals, can be positioned as a gentle, comprehensive daily foundational support product. This leverages clinically studied tolerability and cellular retention for claims, while the added calcium provides a secondary bone health benefit, appealing to a broader wellness audience.
- Electrolyte & Hydration Enhancement: In the booming sports and hydration category, sodium ascorbate is a functionally integrated ingredient. It delivers antioxidant support to combat exercise-induced oxidative stress while concurrently contributing bioavailable sodium to electrolyte blends. This dual function maximizes ingredient efficiency, simplifies the formula, and supports claims focused on recovery and rehydration.
- Gentle Nutraceuticals for Sensitive Demographics: Targeting aging populations or consumers with sensitive GI tracts is a key market strategy. Calcium ascorbate is the clear candidate for this segment. Its non-acidic nature directly addresses gastric sensitivity concerns, while the included calcium supports bone and muscular health—two top priorities for older adults. This allows for powerful "gentle on the stomach, strong on support" claims rooted in formulation science.
From Insight to Ingredient: Making the Informed Choice
The final, critical step is translating your selected form into a reliably sourced, high-quality ingredient. The theoretical advantages of a specific ascorbate are nullified by inconsistent, impure, or poorly documented bulk material.
For procurement and R&D teams, the supplier selection checklist must extend beyond the basic Certificate of Analysis. It should encompass:
- Comprehensive Technical Dossiers: Including stability data (shelf life under various temperature/humidity conditions), compatibility studies, and application notes.
- Quality Assurance: Evidence of rigorous batch-to-batch consistency via modern analytical methods like HPLC, ensuring potency specifications are met every time.
- Regulatory & Compliance Readiness: Documentation proving manufacture in a GMP-certified facility, along with support for relevant regulatory status (e.g., USP, FCC, FDA GRAS, EFSA, TGA compliance) for your target markets.
- Technical Partnership: The supplier's ability to act as a problem-solving partner, offering insights on application-specific challenges such as optimal particle size for blending, dissolution rates for tableting, or stability in novel delivery systems.
Does your current ingredient partner provide this level of data integrity and collaborative support? The quality and consistency of your raw material are the non-negotiable foundation for your product's safety, efficacy, and commercial viability.
Conclusion: Precision as a Competitive Advantage
In today's saturated health market, differentiation is engineered through formulation intelligence. The strategic selection between ascorbic acid, sodium ascorbate, and calcium ascorbate exemplifies how a deep understanding of ingredient science creates tangible product value and defensible market positioning. This precision enables brands to move beyond generic vitamin C claims to make specific, evidence-based promises about superior tolerability, enhanced stability, targeted nutrient delivery, and optimized consumer experience. Such precision builds authentic brand trust, commands potential price premiums, and drives long-term consumer loyalty in the competitive B2B landscape.
To translate this knowledge into a concrete product innovation, begin with the raw material. We have prepared a detailed technical dossier that expands on the application data, stability considerations, and compatibility guidelines for each vitamin C form. This resource is designed to help you model the integration of these ingredients into your specific formulation pipeline.
To inform your next development cycle, you can request the complete Vitamin C Formulation Guide & Technical Dossier. This document provides the granular data needed to make a confident, informed sourcing decision for your upcoming project.
Share this article
Found this helpful? Share it with others!
Related Products
Products mentioned in this article
Want to learn more?
Explore our products or contact our team for personalized solutions and expert advice.